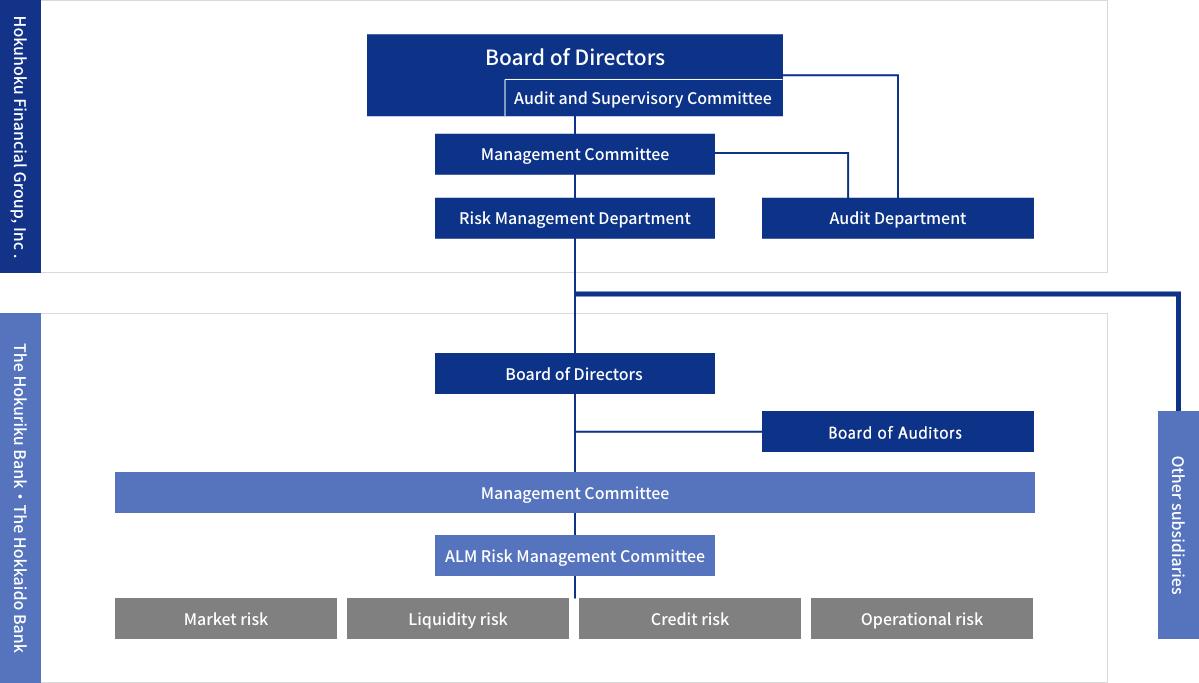
We work to establish an appropriate risk management system in accordance with the scale and type of risk.
Integrated risk management framework
The company group has established a basic risk management policy for various risks and is striving for the establishment of an integrated risk management framework to ensure risk taking and management resource allocation balanced with earnings targets while keeping overall levels of risk within the group’s managerial capacity to ensure the protection of customer deposits and the trust of shareholders and creditors.
In addition, we have established an integrated Risk Management Department to integrate and manage various risks, while the independent Audit Department carries out internal audits and we have a framework that verifies the appropriateness and effectiveness of risk management system.
Allocation of risk capital
The company group quantifies the various risks generated with respect to its operations as uniformly as possible and manages risk so that the overall level of risk is kept within the group’s management capacity.
The subsidiary banks estimate maximum potential losses by quantifying credit risk, market risk and operational risk, allocate risk capital sourced from core capital to make effective use of capital resources, and control and manage risk within the range permissible for management.
Meanwhile, the company manages risk so that excessively large risks are not taken relative to capital on a group-wide basis, such as verifying the risk allocation plans of subsidiary banks, and whether amounts in excess of risk capital allocations are sufficient to cover risk conceivably affecting subsidiaries other than the subsidiary banks as well as risk not included in the risk assumptions, and monitoring actual levels of risk.
In addition, we perform stress tests to calculate the extent of potential losses that would be anticipated in certain scenarios such as a normally inconceivable deterioration of business conditions or market fluctuations. By doing so, we verify regularly the substantiality of our capital position against risk.
Credit risk management
-
Basic approach
Credit risk involves means the risk that it will become impossible to recover the principal or interest of loans, etc., due to a reason such as the deterioration of a customer’s management situation. Although this is an unavoidable risk for a bank, whose mission is financial mediation, the company group strives to develop and strengthen its credit risk management systems to maintain and enhance the soundness of its assets.
-
Credit risk management systems
To maintain and enhance the soundness of assets, the company group strives to grasp credit risk promptly and accurately using its internal ratings system and asset self-assessment, and performs appropriate write-offs and provisions to reserves.
When making individual judgements on the granting of credit, we carry out rigorous screening in accordance with the standards and principles specified in our credit policy.
-
Internal ratings systems
To grasp the credit risk of loans, etc., objectively, our subsidiary banks have introduced internal ratings systems. They grasp trends in ratings continuously by breaking customers’ creditworthiness down into fifteen levels based on financial data and qualitative information.
In addition, we monitor the credit concentration status of large borrowers based on the Group Management Rules for Credit Limits and manage loans so that no excessive credit concentration risk arises.
-
Self-assessment standards
Self-assessments are implemented strictly by asset assessment departments at the subsidiary banks based on the self-assessment standards, and their appropriateness is verified by Risk Management Department and an independent internal management department.
-
Corporate rehabilitation
After making a loan to a corporate customer, we strive to prevent bad debt from occurring by assessing the business conditions faced by the borrower and following up their business plans. Meanwhile, we strive for the soundness of assets through the creation of a framework dedicated to the management of bad debt and the strengthening of support functions for corporate rehabilitation.
Market risk management
-
Basic approach
Market risk means the risk of incurring losses due to fluctuations in the value of assets and liabilities held or in earnings generated caused by fluctuations in various market risk factors such as interest rates, stock prices and foreign exchange rates.
The company group strives to control market risk appropriately and manage operations so that we can ensure stable earnings.
To that end, at the subsidiary banks that mainly handle transactions involving market risk, we have established regulations for market risk management and manage assets and liabilities comprehensively (ALM).
Liquidity risk management
Liquidity risk includes fund procurement risk involving losses that may be incurred by being unable to procure funds due to a decline in creditworthiness, etc., and being forced to procure funds at a significantly higher interest rate than normal, and market liquidity risk involving losses that may be incurred due to market disorder, etc., preventing a company from trading or forcing it to trade on considerably less favorable cost than normal.
The subsidiary banks, which account for a majority of the group’s liquidity risk, have stipulated regulations on liquidity risk management and maintain adequate levels of government bonds and other payment reserve assets that are readily convertible into cash. They also set various management indices and monitor these on a daily basis. The state of liquidity risk is reported and discussed regularly at meetings of the ALM Risk Management Committee, etc., so that we will be able to respond appropriately should a crisis occur.
The company grasps the state of management and procurement at subsidiary banks, and takes every precaution possible for smooth fund procurement.
Operational risk management
-
Basic approach
Operational risk means the risk of losses that may arise as a result of operational processes, the conduct of executives or employees, or computer systems being inappropriate, or adverse external events.
The company group has established Rules for the Management of Operational Risk and categorizes operational risk into seven categories: 1) administrative risk; 2) system risk; 3) legal risk; 4) human risk; 5) tangible asset risk; 6) reputational risk; and 7) other risks. The state of these risks is monitored by the Operational Risk Specialist Committee, which convenes each month at the subsidiary banks, and we strive to establish a PDCA cycle framework by grasping potential risks through risk assessments, etc., and evaluating preventive measures.
-
Risk management systems by major category
Administrative risk management
The company group considers measures to prevent reoccurrence through analysis of the causes of administrative errors and other incidents, advances the centralization and streamlining of administrative processing at headquarters from the perspectives of consolidation and mutual checks and strives to implement initiatives aimed at reducing administrative risk.
System risk management
The company group has formulated Rules for System Risk Management and a basic policy on ensuring the safety of information assets (security policy), has established a robust management and operating framework, and implements various security management measures, including backup systems. In addition, we are working on the strengthening of the security management framework aimed at responding promptly to cyberattacks, which have tended to increase in recent years.
Crisis management
To minimize the impact of any large-scale disaster or other emergency, should one occur, the company group has formulated a “Crisis management manual (contingency plans, etc.)” and has also established a framework for information-gathering and the centralization of instructions and commands in the event of a crisis.
In particular, the subsidiary banks have established a “Business continuity plan (BCP),” so that they can continue the settlement functions and other work required of financial institutions in the event an earthquake, infections or other crisis occurs, and have also established a framework that will allow them to respond thoroughly to any crisis situation.